What Is the Role of Cryptography in Cybersecurity?
Explore the crucial role of cryptography in cybersecurity, including encryption, digital signatures, secure communications, and data protection. Learn how cryptography safeguards information, prevents unauthorized access, and ensures data integrity in today's digital world.
Introduction
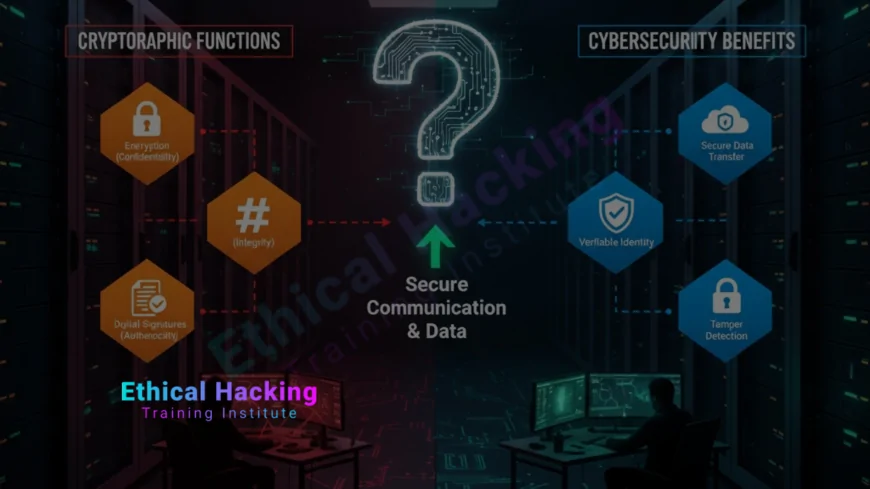
Cryptography is a foundational pillar of cybersecurity that ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of digital information. In a world where cyber attacks are increasingly sophisticated, understanding the role of cryptography is essential for both security professionals and everyday users. It provides the tools and techniques to protect sensitive data, authenticate users, and secure communications against unauthorized access or tampering.
Understanding Cryptography
At its core, cryptography involves transforming readable data into an unreadable format using algorithms. The main objectives include:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring only authorized parties can access information.
- Integrity: Verifying that data has not been altered.
- Authentication: Confirming the identities of parties involved.
- Non-repudiation: Preventing denial of actions or transactions.
There are two primary types of cryptography: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. Advanced cybersecurity professionals often combine these methods for enhanced security.
How Cryptography Protects Data
Cryptography ensures that sensitive information, whether stored or in transit, remains secure. For example:
- Encrypting files on a computer or server prevents unauthorized users from reading the data.
- Using encrypted communication protocols like SSL and TLS secures internet connections.
- Digital signatures verify the authenticity and integrity of messages and documents.
These techniques are crucial for protecting financial data, personal information, and corporate secrets from cybercriminals and hackers, especially in industries with high regulatory requirements.
Cryptography in Network Security
In network security, cryptography plays a vital role in securing communications. Techniques like VPNs, SSL/TLS, and IPsec encrypt data traffic, preventing eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Network security tools often integrate cryptographic algorithms to protect transmitted data, authenticate devices, and maintain secure channels between endpoints. Professionals can also leverage knowledge from ethical hacking courses to understand vulnerabilities and apply cryptography effectively.
Cryptography in Cybersecurity Tools
Many cybersecurity tools and practices rely on cryptography for protection and verification. Examples include:
- Password hashing and salting to protect user credentials
- Encryption of databases and cloud storage
- Secure email protocols like PGP for confidential communication
- Digital certificates for authenticating websites and applications
Understanding these tools allows security professionals to select the right solutions and configure them correctly to mitigate cyber risks.
Role in Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing
Ethical hackers must understand cryptography to identify potential weaknesses and ensure proper security implementation. Techniques such as key cracking, cipher analysis, and exploiting weak encryption algorithms are explored in penetration testing. Learning through structured programs or courses helps professionals identify vulnerabilities and apply mitigation strategies, strengthening overall cybersecurity posture.
Cryptography in Data Integrity and Authentication
Maintaining data integrity ensures that information is not altered during storage or transmission. Cryptographic hashing, digital signatures, and certificates provide mechanisms to verify data authenticity. Organizations rely on these techniques to secure financial transactions, software updates, and critical communications. Advanced cryptographic methods help prevent tampering and provide evidence for auditing purposes.
Emerging Trends in Cryptography
As cyber threats evolve, cryptography continues to advance. Emerging trends include:
- Post-quantum cryptography to resist quantum computer attacks
- Homomorphic encryption enabling computations on encrypted data
- Blockchain and decentralized security leveraging cryptographic protocols
- AI-assisted cryptography for adaptive security
Professionals can stay ahead of threats by following cutting-edge cryptographic research and applying best practices learned from AI-driven security insights.
Best Practices for Using Cryptography in Cybersecurity
Implementing cryptography effectively requires adhering to best practices:
- Use strong, well-tested algorithms and avoid deprecated methods
- Properly manage and protect cryptographic keys
- Regularly update protocols and encryption standards
- Combine cryptography with other security measures like access control and monitoring
Following these practices ensures robust protection against data breaches and unauthorized access.
Conclusion
Cryptography is essential in cybersecurity, providing confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation. It protects data at rest and in transit, secures communications, and ensures authenticity in digital interactions. Understanding cryptographic techniques and implementing them properly is critical for professionals, businesses, and individuals aiming to safeguard sensitive information in the digital age. Integrating cryptography with other security measures and continuous learning ensures strong, resilient defenses against evolving cyber threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cryptography?
Cryptography is the practice of securing information by transforming it into unreadable formats and controlling access through algorithms and keys.
Why is cryptography important in cybersecurity?
It ensures data confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and tampering.
What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric cryptography?
Symmetric cryptography uses a single key for encryption and decryption, while asymmetric cryptography uses a public-private key pair.
How does cryptography protect communications online?
Protocols like SSL, TLS, and VPNs encrypt data transmitted over networks, preventing interception and unauthorized access.
What are digital signatures?
Digital signatures verify the authenticity and integrity of messages or documents using cryptographic algorithms.
Can cryptography prevent malware attacks?
While cryptography does not directly stop malware, it protects sensitive data from being stolen or tampered with by malicious software.
What is hashing?
Hashing is a cryptographic technique that converts data into a fixed-length string, used to verify data integrity.
How is cryptography used in ethical hacking?
Ethical hackers analyze encryption and security mechanisms to identify vulnerabilities and test defenses in controlled environments.
What is the role of PKI in cybersecurity?
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) manages digital certificates and keys, ensuring secure authentication and data exchange.
What are common cryptographic algorithms?
Common algorithms include AES, RSA, SHA, and ECC, each used for encryption, signing, or hashing.
How can individuals use cryptography for personal security?
Using encrypted messaging, secure passwords, two-factor authentication, and VPNs helps individuals protect personal data.
What is homomorphic encryption?
Homomorphic encryption allows computations on encrypted data without decrypting it, preserving privacy during processing.
How does cryptography relate to blockchain?
Blockchain uses cryptographic hashing and digital signatures to ensure data integrity, authenticity, and trust in distributed systems.
Can AI assist in cryptography?
Yes, AI can help optimize encryption algorithms, detect weaknesses, and adapt security measures to emerging threats.
Where can I learn more about cryptography in cybersecurity?
Online courses, practical labs, and ethical hacking programs from trusted institutes provide hands-on learning and in-depth understanding of cryptography and its applications.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0