How Do Hackers Hack Wi-Fi Networks?
Learn exactly how hackers break into Wi-Fi networks using simple tools and common mistakes. This beginner-friendly guide reveals real techniques, tools, and step-by-step methods attackers use in 2025, so you can protect your home or business network from unauthorized access.
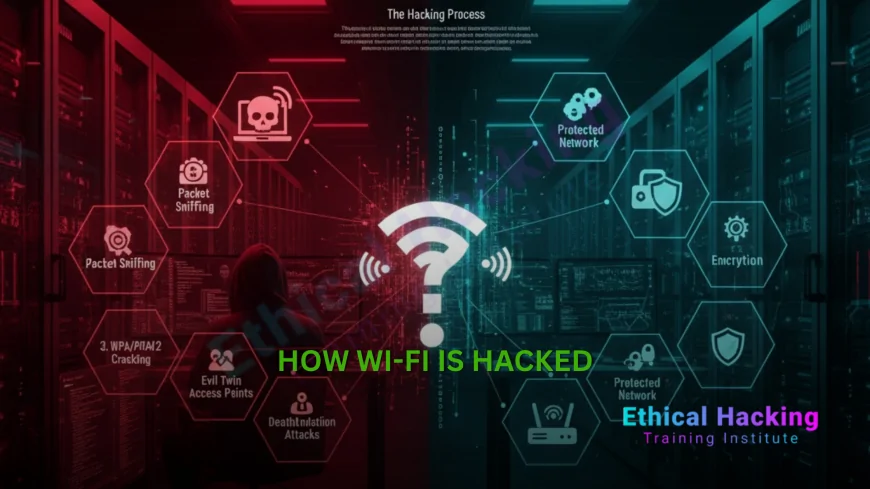
Introduction: Your Wi-Fi Is More Vulnerable Than You Think
Every day, millions of people connect to Wi-Fi at home, work, or coffee shops. It’s fast, convenient, and invisible. But that invisibility is exactly what makes Wi-Fi a prime target for hackers.
In 2025, hacking Wi-Fi doesn’t require a hoodie or supercomputer. With a $50 device and free software, anyone can attempt to break in. The good news? Most attacks rely on weak passwords, outdated settings, or user mistakes. This means you can stop them.
This guide explains how hackers actually hack Wi-Fi networks, using real-world techniques and tools. You’ll learn their methods not to attack, but to defend. Let’s secure your connection before someone else does.
Step 1: Understanding How Wi-Fi Security Works
Before hacking, attackers study how Wi-Fi protects itself. Here are the main security types:
| Protocol | Security Level | Status in 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| WEP | Very Weak | Cracked in minutes, avoid completely |
| WPA | Weak | Rarely used, easily broken |
| WPA2 | Moderate | Still common, vulnerable to some attacks |
| WPA3 | Strong | Best protection, use if available |
Hackers target older protocols (WEP, WPA, WPA2) because they have known flaws. WPA3 fixes most, but many routers still run WPA2.
Step 2: Finding and Targeting a Wi-Fi Network
Hackers don’t guess. They scan for networks using simple tools.
Tools Used
- Laptop with Wi-Fi adapter in monitor mode
- Free software: Aircrack-ng, Wireshark, Kismet
- Android apps like WiFi Analyzer (for scouting)
How They Scan
They walk or drive around (called “wardriving”) and collect:
- Network name (SSID)
- Signal strength
- Encryption type
- Channel and MAC address
They look for weak signals, hidden SSIDs, or default router names (like “NETGEAR57”) that hint at poor setup.
Want to see networks like a hacker? Start with an ethical bootcamp and learn safe scanning techniques.
Attack Method 1: Cracking the Password (Brute Force & Dictionary)
The most common way to hack Wi-Fi: guess the password.
How It Works
- Hacker captures the “handshake” when a real device connects
- Uses wordlists (millions of common passwords)
- Tests each one offline using GPU power
Tools
- Aircrack-ng
- Hashcat
- Custom wordlists (rockyou.txt, weakpass)
Time to Crack
| Password | Crack Time |
|---|---|
| 12345678 | Seconds |
| password123 | Minutes |
| MyDogName2023 | Hours to days |
| 14-random-characters | Years (impossible) |
Attack Method 2: Deauthentication Attack (Kick Devices Off)
Hackers force your phone or laptop off the network to capture the handshake.
Steps
- Send fake “disconnect” packets to your device
- Your device automatically reconnects and reveals handshake
- Hacker captures it and cracks offline
Tool
Aireplay-ng (part of Aircrack-ng suite)
This attack works even if you never interact. Just being connected is enough.
Practice this safely in a lab. Enroll in CEH practical training to master controlled Wi-Fi testing.
Attack Method 3: Evil Twin Access Point
Hacker creates a fake Wi-Fi hotspot with the same name as yours.
How It Works
- Sets up rogue AP with stronger signal
- Your phone auto-connects to the fake one
- All traffic goes through hacker’s device
- They steal logins, files, or inject malware
Common Locations
- Coffee shops
- Airports
- Hotels
Tools
- Fluxion
- WiFi Pineapple
- Linux laptop with Hostapd
Never connect to “Free_WiFi” or networks without passwords.
Attack Method 4: Exploiting WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
WPS lets you connect by pressing a button or entering an 8-digit PIN.
Weakness
The PIN is split into two 4-digit parts. Only 11,000 combinations to guess.
Attack Tool
Reaver or Bully
Time to Crack
4 to 10 hours max.
Many routers still have WPS enabled by default. Disable it immediately.
Go beyond defense. Learn CEH online and perform your own WPS audits legally.
Attack Method 5: KRACK and PMKID Attacks (Advanced)
These exploit flaws in WPA2 itself.
KRACK (Key Reinstallation Attack)
Forces reuse of encryption keys. Allows decryption of traffic.
PMKID Attack
Captures handshake without any connected devices. Works on many routers.
Tools
- hcxdumptool + hashcat
- KRACK attack scripts
Most devices are patched, but old routers remain vulnerable.
Attack Method 6: Router Admin Panel Attacks
Hackers don’t always crack Wi-Fi. They log into your router.
Common Tricks
- Default passwords (admin/admin)
- DNS hijacking via public Wi-Fi
- Phishing pages that look like router login
Once Inside
- Change Wi-Fi password
- Disable security
- Redirect your traffic
Always change default router login and use strong admin passwords.
Want to find open ports and weak configs? Use Nmap mastery to scan your own network first.
How to Protect Your Wi-Fi from All These Attacks
Prevention is simple. Follow this checklist:
- Use WPA3 (or WPA2-AES if unavailable)
- Set a strong password: 16+ random characters
- Disable WPS
- Hide your SSID (optional, but helps)
- Change default router login
- Enable MAC filtering (allow only known devices)
- Update router firmware monthly
- Use guest network for visitors
- Turn off Wi-Fi when not in use
- Monitor connected devices
Conclusion: Secure Wi-Fi Is Easy If You Act Now
Hackers don’t need magic. They use free tools, patience, and your mistakes. But every attack in this guide fails against a properly secured network.
Take 10 minutes today: log into your router, enable WPA3, set a strong password, and disable WPS. That’s it. You’ve just blocked 99 percent of Wi-Fi hackers.
Stay safe online. Your data, privacy, and peace of mind are worth the effort.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can someone hack my Wi-Fi without being nearby?
Usually no. Most attacks need to be in range (100 to 300 feet). But drones or powerful antennas extend this. Strong passwords still protect you.
Is WPA3 completely unhackable?
No security is perfect, but WPA3 fixes major WPA2 flaws. It’s the best available in 2025.
Should I hide my Wi-Fi name (SSID)?
It adds minor security through obscurity. Not required, but recommended. Devices must be manually added.
Can hackers see what I do on Wi-Fi?
Only if they’re on your network or it’s unencrypted. Use HTTPS websites and a VPN for extra safety.
Is it safe to use public Wi-Fi?
Risky. Use a trusted VPN and avoid banking or logins. Assume all traffic is watched.
Does restarting the router stop hackers?
Temporarily disrupts some attacks, but not a solution. Change passwords and settings instead.
Can smart TVs or printers be used to hack Wi-Fi?
Yes, if they have weak firmware. Keep all devices updated and isolate IoT on a guest network.
How do I know if my Wi-Fi is hacked?
Signs: slow speed, unknown devices in router list, strange pop-ups, high data usage.
Is WPS really that dangerous?
Yes. An 8-digit PIN is guessable in hours. Disable WPS on all routers.
Can I use the same password for Wi-Fi and router login?
No. Use different strong passwords. If one is cracked, the other stays safe.
Do I need antivirus on my router?
Some modern routers have built-in security (like NETGEAR Armor). Otherwise, protect each device.
Is it illegal to test my own Wi-Fi?
No, testing your own network is legal and encouraged. Never test networks you don’t own.
Can hackers hack Wi-Fi through walls?
Yes, signals pass through walls. Physical distance matters more than obstacles.
Should I change my Wi-Fi password regularly?
Only if you suspect compromise. A strong password doesn’t need frequent changes.
What’s the safest Wi-Fi setup for home?
WPA3, 20+ character random password, WPS off, guest network, firmware updated, strong admin login.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
9
Like
9
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
4
Love
4
 Funny
1
Funny
1
 Angry
2
Angry
2
 Sad
5
Sad
5
 Wow
4
Wow
4