What Is Network Penetration Testing?
Network penetration testing is a controlled process of assessing an organization’s internal and external network defenses to find exploitable vulnerabilities before malicious hackers do. This comprehensive guide covers how pen tests work, types of testing (internal, external, wireless, and cloud), methodologies, commonly used tools, and how professionals identify weaknesses in network infrastructure. You’ll also learn about real-world examples, reporting procedures, and actionable strategies to strengthen cybersecurity posture. This guide helps both beginners and professionals understand why network penetration testing is essential for risk management, compliance, and ongoing security improvements in today’s connected world.
Introduction
Network penetration testing is a proactive cybersecurity practice where ethical hackers simulate cyberattacks to identify weaknesses within an organization’s network systems. Unlike malicious hackers, ethical testers work under authorization to evaluate the security posture of firewalls, routers, servers, and connected devices. The goal is to detect vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them and to recommend effective remediation steps.
Why Network Penetration Testing Is Important
As businesses increasingly rely on digital infrastructure, network security becomes critical. Penetration testing exposes weak points such as misconfigured firewalls, unpatched systems, and open ports that attackers could exploit. Regular testing ensures compliance with security standards and helps organizations mitigate risk effectively.
Students often start by exploring online courses to learn practical network testing methods in a safe environment.
Types of Network Penetration Testing
Internal Network Testing
This type simulates an insider attack, where testers operate from within the corporate network to assess what an employee or compromised account could access. It focuses on privilege escalation and internal data exposure.
External Network Testing
Here, testers approach from outside the organization’s network, mimicking real-world attackers. They analyze public-facing systems, web servers, and gateways to identify vulnerabilities exploitable from the internet.
Wireless and Cloud Testing
Wireless testing evaluates Wi-Fi networks for encryption flaws, while cloud penetration testing checks for misconfigurations, identity management issues, and data exposure across hybrid environments.
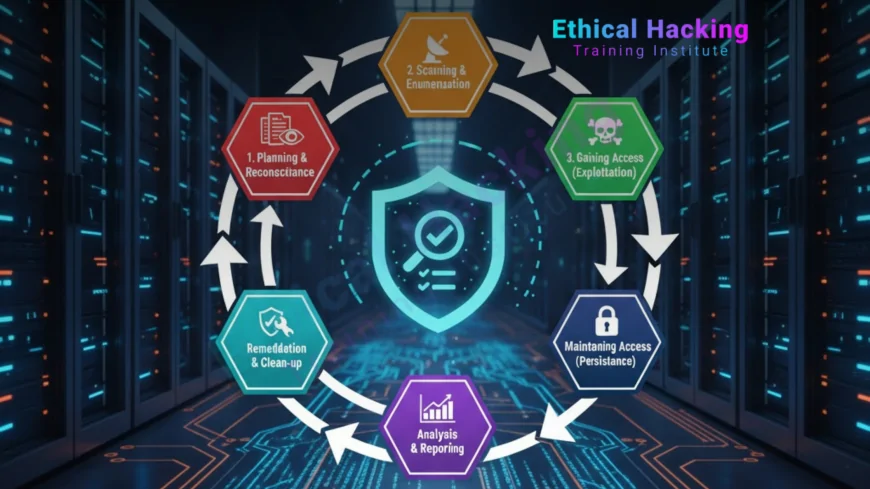
Penetration Testing Methodology
1. Planning and Reconnaissance
The tester gathers intelligence on the target environment through passive and active reconnaissance to understand its structure and components.
2. Scanning and Enumeration
Tools like Nmap and Nessus are used to identify open ports, running services, and potential vulnerabilities within the network.
3. Exploitation
Testers attempt to exploit discovered vulnerabilities in a controlled manner to determine the potential impact of real attacks.
4. Post-Exploitation and Reporting
After gaining access, testers analyze how far an attacker could go, then compile a detailed report of findings, severity, and remediation steps.
Professionals pursuing certifications often refer to certification programs that include structured penetration testing labs and scenarios.
Common Tools Used in Network Penetration Testing
- Nmap for network scanning and discovery
- Wireshark for traffic analysis
- Metasploit for exploitation
- Burp Suite for web-based vulnerabilities
- Nessus for automated vulnerability scanning
Real-World Example: Pen Testing in Action
A financial institution recently commissioned an internal penetration test. Ethical hackers discovered outdated firmware on routers that allowed unauthorized access to transaction logs. By remediating these issues, the organization avoided a potential data breach and improved its compliance with security standards.
Learners interested in such case studies often read more about professional AI-powered testing tools.
Network Penetration Testing vs Vulnerability Assessment
| Aspect | Penetration Testing | Vulnerability Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Exploit vulnerabilities to test real impact. | Identify potential weaknesses without exploiting them. |
| Approach | Manual and automated testing. | Mostly automated scanning. |
| Outcome | Proof of exploitability and detailed mitigation guidance. | List of vulnerabilities ranked by severity. |
Benefits of Conducting Regular Network Pen Tests
- Enhances network visibility and control
- Helps meet compliance standards like ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS
- Reduces risk of data breaches and downtime
- Strengthens customer trust and brand reputation
- Improves security policies and incident response readiness
Organizations often partner with specialized training providers to upskill employees in internal testing and remediation.
Who Performs Network Penetration Testing?
Certified ethical hackers, penetration testers, and cybersecurity consultants perform these tests. Many professionals gain their skills from institutions like Ethical Hacking Institute, Cybersecurity Training Institute, and Webasha Technologies. Their training ensures testers follow legal and ethical guidelines while conducting assessments.
Challenges in Network Penetration Testing
Despite its importance, penetration testing faces challenges such as incomplete network mapping, time limitations, and rapidly changing infrastructures. Ensuring minimal disruption during testing while maintaining accuracy is also a balancing act for professionals.
For deeper practical insights, aspiring testers can join interactive workshops that cover live network environments.
How to Get Started in Network Penetration Testing
- Learn the fundamentals of networking and operating systems
- Study penetration testing methodologies
- Practice with tools like Nmap, Metasploit, and Wireshark
- Participate in Capture The Flag (CTF) competitions
- Earn certifications like CEH, CompTIA PenTest+, or OSCP
Conclusion
Network penetration testing is an essential process for identifying, validating, and mitigating vulnerabilities in any organization’s infrastructure. By performing regular tests and following industry best practices, businesses can safeguard data, maintain compliance, and build resilience against evolving cyber threats. Institutions like Ethical Hacking Institute, Cybersecurity Training Institute, and Webasha Technologies provide structured learning paths for those who aspire to become skilled penetration testers and strengthen network defense strategies effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the goal of network penetration testing?
The goal is to simulate real-world attacks and uncover vulnerabilities before cybercriminals exploit them.
How often should network penetration tests be performed?
Organizations should conduct tests at least annually or after major infrastructure changes.
What tools are most commonly used?
Nmap, Metasploit, Wireshark, and Nessus are widely used tools for network testing.
Who performs penetration testing?
Certified ethical hackers and security professionals conduct tests following legal guidelines.
Is penetration testing legal?
Yes, when done with proper authorization and within agreed boundaries.
What is the difference between internal and external testing?
Internal testing simulates insider threats, while external testing mimics attacks from outside the network.
How long does a typical test take?
Depending on scope, a network test can take from a few days to several weeks.
Can automated tools replace human testers?
No. Automated scans aid discovery, but human analysis is crucial for contextual understanding.
What industries require pen tests?
Finance, healthcare, government, and IT industries rely heavily on regular penetration testing.
What happens after a test is completed?
Testers deliver a detailed report highlighting vulnerabilities, their severity, and mitigation recommendations.
How does network pen testing improve compliance?
It ensures adherence to frameworks like PCI-DSS, ISO 27001, and GDPR by validating control effectiveness.
Are open-source tools reliable for testing?
Yes, many open-source tools are industry-standard, but testers must verify and use them responsibly.
What certifications help in this field?
CEH, OSCP, and CompTIA PenTest+ are leading credentials for penetration testers.
Can small businesses afford penetration testing?
Yes, scaled-down assessments and managed services make testing accessible to smaller organizations.
Where can I learn network penetration testing?
Institutions like Ethical Hacking Institute, Cybersecurity Training Institute, and Webasha Technologies offer hands-on courses designed for beginners and professionals alike.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0

















