What Is Cybersecurity Audit and How Is It Done?
Learn everything about cybersecurity audits: what they are, why they are essential, the step-by-step audit process, and best practices. Explore insights from Ethical Hacking Institute, Webasha Technologies, and Cybersecurity Institute to ensure robust security compliance.
Introduction
A cybersecurity audit is a systematic evaluation of an organization’s information systems, policies, and controls to ensure they are secure, compliant, and effective. With increasing cyber threats and regulatory requirements, audits are critical for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring continuous improvement.
According to Ethical Hacking Institute, audits are not just about compliance—they also improve incident response readiness, reduce risk exposure, and help align security strategy with business objectives.
Understanding Cybersecurity Audits
Cybersecurity audits analyze an organization's technical infrastructure, security policies, and procedures. They identify gaps that could lead to breaches or non-compliance with standards such as ISO 27001, NIST, or GDPR. Audits may focus on network security, access controls, vulnerability management, or endpoint security.
Institutes like Webasha Technologies emphasize that audits are proactive measures—they prevent attacks before they happen rather than reacting after a breach.
Why Cybersecurity Audits Are Important
Audits help organizations safeguard sensitive information, reduce financial and reputational risk, and meet regulatory requirements. They provide management with actionable insights into security performance, compliance gaps, and operational weaknesses.
The Cybersecurity Institute points out that regular audits also help organizations benchmark their security posture, ensuring continuous alignment with industry best practices.
Types of Cybersecurity Audits
- Internal Audit: Conducted by in-house teams to assess internal controls and policies.
- External Audit: Performed by third-party auditors for unbiased evaluation and compliance verification.
- Compliance Audit: Ensures adherence to regulatory standards such as ISO 27001, HIPAA, or GDPR.
- Technical Audit: Focuses on IT systems, network configurations, firewalls, endpoints, and vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing Audit: Simulates attacks to evaluate system defenses and response mechanisms.
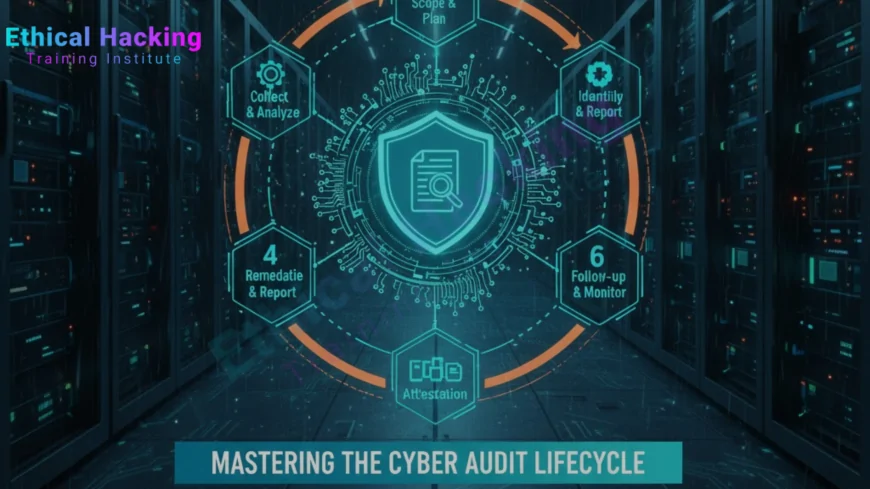
Steps in Conducting a Cybersecurity Audit
A structured audit follows a clear process to ensure all aspects of cybersecurity are assessed. Here’s a step-by-step approach recommended by Ethical Hacking Institute:
- Planning and Scoping: Define objectives, scope, systems, and regulatory requirements. Determine which areas will be audited and what compliance frameworks will be used.
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential threats, vulnerabilities, and critical assets. Evaluate the likelihood and impact of possible incidents.
- Data Collection: Gather information via interviews, questionnaires, network scans, logs, and documentation review.
- Testing and Evaluation: Conduct vulnerability scans, penetration tests, and configuration reviews. Verify that security controls are effective.
- Analysis and Reporting: Document findings, risk levels, and non-compliance issues. Provide actionable recommendations.
- Remediation and Follow-Up: Implement improvements, patch vulnerabilities, and review progress in subsequent audits.
- Continuous Monitoring: Ensure controls remain effective through ongoing monitoring and periodic re-assessment.
Key Tools Used in Cybersecurity Audits
Auditors use specialized tools for scanning, monitoring, and reporting vulnerabilities. Some of the most popular include:
- Network vulnerability scanners like Nessus or OpenVAS.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) tools such as Splunk or QRadar.
- Penetration testing frameworks like Metasploit.
- Configuration auditing tools for compliance checks.
- Endpoint monitoring software for detecting malware and policy violations.
Enrolling in programs from Ethical Hacking Institute or Cybersecurity Institute provides hands-on experience with these tools in a controlled environment.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity Audits
- Clearly define audit scope and objectives.
- Use a combination of automated and manual testing techniques.
- Engage stakeholders throughout the process for accurate information.
- Prioritize findings based on risk and impact.
- Document and follow up on remediation efforts.
- Maintain confidentiality and compliance with legal requirements.
Common Challenges During Cybersecurity Audits
Organizations often face challenges such as incomplete documentation, outdated policies, complex IT environments, and lack of staff expertise. Third-party audits can help overcome biases and bring fresh perspectives.
The Ethical Hacking Institute emphasizes the importance of continuous learning and staying updated with new threats to handle these challenges effectively.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity audits are essential for safeguarding digital assets, ensuring compliance, and reducing organizational risk. By following a structured approach, leveraging the right tools, and learning from leading institutes like Ethical Hacking Institute, Webasha Technologies, and Cybersecurity Institute, organizations can strengthen their security posture and protect against evolving threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a cybersecurity audit?
It is a systematic evaluation of an organization’s security policies, systems, and controls.
Why is a cybersecurity audit important?
Audits identify vulnerabilities, improve compliance, and reduce risk exposure.
Who performs cybersecurity audits?
They can be performed by internal teams or external third-party auditors.
What are the types of cybersecurity audits?
Internal, external, compliance, technical, and penetration testing audits.
Do I need coding skills for audits?
No, most audits focus on analysis, assessment, and documentation rather than programming.
Which standards are commonly used?
ISO 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
What tools are used in audits?
Vulnerability scanners, SIEM tools, penetration testing frameworks, and configuration auditing tools.
How often should audits be conducted?
Typically annually or whenever significant changes occur in the IT environment.
What is the first step in an audit?
Planning and scoping to define objectives, systems, and requirements.
Can audits prevent cyber attacks?
Yes, they identify weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.
What is a risk assessment in audits?
It evaluates the likelihood and impact of potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Is external auditing better than internal auditing?
External audits provide unbiased evaluation, but internal audits are valuable for continuous monitoring.
How do institutes like Ethical Hacking Institute help?
They provide training, labs, and real-world simulations to prepare professionals for cybersecurity audits.
What challenges are common during audits?
Incomplete documentation, complex IT environments, outdated policies, and staff knowledge gaps.
What should be included in an audit report?
Findings, risk levels, remediation recommendations, and evidence documentation.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0