What Are the Differences Between CEH, OSCP, and CISSP?
Compare CEH, OSCP, and CISSP to decide the best certification for your cybersecurity career. This guide explains syllabus, difficulty, prerequisites, exam style, career outcomes, costs, study tips, and which path suits beginners, technical testers, and security managers.
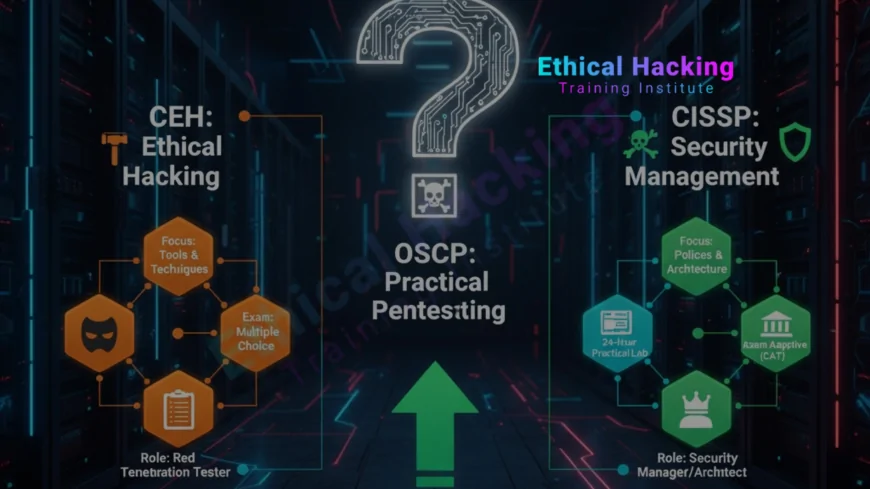
Introduction
Choosing the right cybersecurity certification can shape your career path for years. CEH, OSCP, and CISSP are three of the most visible credentials in the industry, but they serve very different purposes. CEH is commonly seen as an entry to intermediate level certification for ethical hacking concepts. OSCP is a hands on, technical penetration testing certification that tests live exploit development and creative problem solving. CISSP is a management oriented, broad security certification focusing on architecture, governance, risk, and operations. This article compares each across syllabus, exam format, required skills, career outcomes, time and cost investment, and which profile of candidate each best suits.
Overview of the Three Certifications
At a glance, the three certifications differ in focus and intended audience. CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) covers common hacking techniques and tools and is often used by security enthusiasts and junior pentesters to validate knowledge. OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional) is a performance based credential requiring you to hack into multiple live machines in a lab, produce proof, and write a detailed report. CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) is offered by (ISC)² and targets security practitioners aiming for managerial, architect, or policy roles, covering eight domains of security practice.
A practical way to begin is by understanding basic reconnaissance and scanning workflows, such as using a tool like Nmap to map targets, because the reconnaissance phase is common to both ethical hacking and penetration testing curricula.
CEH: What It Covers and Who It’s For
CEH focuses on the tools, techniques, and concepts used by malicious hackers but taught for defensive purposes. Typical topics include footprinting, scanning, enumeration, system hacking, malware, sniffing, social engineering, web server and web application attacks, SQL injection, session hijacking, wireless hacking, and basics of cryptography. The exam is multiple choice and measures familiarity with a large set of topics rather than deep exploit development skills.
CEH is suited to security generalists, help desk staff transitioning to security, and those aiming to demonstrate a formal understanding of hacking methods. Employers sometimes expect CEH as evidence of a baseline skill set. For guided CEH preparation and course structure, many candidates follow formal CEH training that organizes topics and labs.
OSCP: Hands On, Lab Focused Penetration Testing
OSCP is delivered by Offensive Security and is renowned for its practical exam. Instead of multiple choice, exam takers are given a lab network with multiple machines to exploit within a controlled timeframe. They must obtain proof of compromise and submit a professional report describing techniques used, evidence, and remediation suggestions. OSCP emphasizes real world problem solving, pivoting, creative exploitation, and post exploitation skills such as privilege escalation and lateral movement.
The OSCP is best for aspiring penetration testers and technical offensive security professionals who enjoy hands on work and building exploits. Passing OSCP demonstrates the ability to carry out a complete engagement from reconnaissance to exploitation and reporting. Many learners follow intense lab time and practice written reports as part of OSCP prep. For comparative course offerings and deeper lab exposure, look at curated lists of top CEH and OSCP preparation reviews to pick a study path that fits your learning style.
CISSP: Management, Policy, and Broad Security Domains
CISSP from (ISC)² covers a broad body of knowledge across eight domains: Security and Risk Management, Asset Security, Security Architecture and Engineering, Communication and Network Security, Identity and Access Management, Security Assessment and Testing, Security Operations, and Software Development Security. The exam is lengthy and covers high level design, governance, policy, and operational best practices more than specific exploit techniques. CISSP requires at least five years of cumulative paid work experience in two or more domains, though a degree or endorsement can reduce the experience requirement.
CISSP is aimed at security managers, architects, consultants, and experienced practitioners who are building or overseeing security programs. It signals to employers that you understand information security at an organizational level and can lead policy, compliance, and architecture efforts. For an overview of how CISSP fits career paths and training resources, consider authoritative guides and training programs that map curriculum to job roles.
Comparison Table: CEH vs OSCP vs CISSP
| Aspect | CEH | OSCP | CISSP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Tools and hacking techniques | Practical exploitation, labs | Security management and governance |
| Exam Type | Multiple choice | Hands on lab exam and report | Long multiple choice and advanced item types |
| Prerequisite | None formal, recommended experience helpful | Strong networking and Linux basics recommended | 5 years of work experience in security domains |
| Skill Demonstrated | Knowledge of attack tools and concepts | Practical penetration testing and reporting | Security leadership, policy, design, risk |
| Typical Roles | Junior pentester, security analyst | Penetration tester, red teamer | Security manager, architect, CISO path |
| Renewal / Maintenance | Periodic renewal and CPEs | Limited retakes, labs and retest policies | CPE credits and annual maintenance fees |
Choosing between these depends on whether you want a practical offensive skillset, a broad managerial credential, or a foundational ethical hacking certification.
Exam Structure, Difficulty, and Time Investment
CEH is mostly multiple choice and can be prepared for with a mixture of classroom training, lab practice, and study guides. Many learners complete CEH preparation in a few weeks to a few months depending on prior experience. OSCP requires extensive lab time, often hundreds of hours of practice, and the exam is a 24 hour plus report based test that tests persistence and creativity. CISSP preparation often takes months and requires broad reading across domains; the exam is long and tests conceptual understanding across governance, architecture, and operations. Time investment reflects the depth: OSCP demands intense hands on practice, CISSP demands broad domain knowledge and work experience, CEH is middle ground focused on familiarity with tools and techniques.
Costs and Logistics
Costs vary. CEH exam fees and official training packages have a range depending on provider and region. OSCP training includes lab access and exam attempts packaged by Offensive Security, and higher tiers provide longer lab access at additional cost. CISSP exam fees are set by (ISC)² and there are also training and study materials costs. Beyond exam fees, factor in the value of lab time, courses, and the time you will spend practicing. Employers sometimes sponsor exams and training for staff, and many training providers offer installment plans or bundles that include exam vouchers.
Which Certification Fits Your Career Goals?
Match certification to role and interest. If you enjoy hands on technical work, exploits, and penetration testing, OSCP is a strong signal of capability. If you want to validate hacking knowledge and gain a credential recognised in many hiring contexts, CEH offers a balanced, structured path. If your aim is security leadership, architecture, compliance, or CISO-track work, CISSP aligns with those goals. Many professionals combine certifications over time: a practitioner may start with CEH or OSCP for technical credibility and later pursue CISSP as they move into managerial responsibilities.
For structured learning paths that map certification goals to job roles and training schedules, many learners consult curated course lists and local Programs that offer combined classroom and lab exposure.
Study Tips and Preparation Strategies
Preparation differs by certification. For CEH, build familiarity with common tools, follow labs, and practice multiple choice questions to improve recall. For OSCP, invest heavily in labs, practice enumeration, privilege escalation, and reporting. Practice writing clean, reproducible reports because the exam grade depends on evidence and methodology. For CISSP, study domain concepts, real world case studies, and practice scenario questions that test judgment and design thinking. Across all certifications, create a study plan, allocate consistent hours per week, and use a mix of video, labs, and practice exams. Peer study groups and hands on workshops accelerate learning.
Career Impact and Salary Expectations
Certification can affect hiring and salary. OSCP holders are often considered highly capable pentesters and can command competitive salaries in technical roles. CEH is widely recognized as a baseline for ethical hacking roles and helps candidates get interviews for junior roles. CISSP is often associated with managerial and senior roles and can be a prerequisite for leadership positions, which tends to correlate with higher compensation. Real salary outcomes depend on experience, location, employer size, and role specifics. Combine certification with demonstrable experience, portfolio projects, and strong communication skills to maximize career impact.
Combining Certifications: A Practical Path
Many security professionals benefit from a staged approach. A common path is to start with foundational knowledge and a credential like CEH, move into hands on practice and OSCP to prove technical depth, and later pursue CISSP when transitioning to architecture or leadership. This combination shows technical credibility and strategic understanding, making you valuable in both tactical and management discussions. Employers value candidates who can bridge technical execution and security strategy.
If you need complete end to end training that helps bridge multiple certifications with labs and practice, consider picking a comprehensive Course that prepares candidates for practical and theoretical components.
Conclusion
CEH, OSCP, and CISSP each serve distinct roles in the cybersecurity ecosystem. CEH provides structured exposure to hacking concepts and tools, OSCP proves practical penetration testing skill through rigorous labs and reporting, and CISSP validates deep knowledge of security management and governance for senior roles. Choose based on where you want to focus your career: hands on red team work, a technical consultant role, or leadership and governance. Many professionals pursue more than one certification over time to broaden both technical depth and strategic influence.
Ultimately, the best certification is the one aligned to your interests, the job roles you want, and the skills you plan to use daily. Combine certifications with real projects, labs, and continuous learning to build a resilient and rewarding cybersecurity career.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which certification is easiest: CEH, OSCP, or CISSP?
“Easiest” depends on your background. CEH is primarily knowledge based and may be easier for candidates comfortable with multiple choice exams. OSCP is technically intense and requires significant hands on practice. CISSP requires broad experience and is challenging for those without cross domain exposure.
Can I take OSCP without prior experience?
You can attempt OSCP without formal job experience, but strong networking, Linux, and scripting skills are highly recommended before starting OSCP labs.
Is CEH recognized by employers?
Yes. CEH is widely recognized as evidence of basic ethical hacking knowledge and can help open doors to junior security roles.
Does CISSP require work experience?
Yes. CISSP typically requires five years of relevant work experience across at least two domains, though certain education or credentials may substitute for part of the requirement.
Which certification pays the most?
Pay depends on role and experience. CISSP holders in senior roles often have higher average salaries due to leadership responsibilities, while OSCP holders command strong pay in specialized pentesting roles.
How long does it take to prepare for OSCP?
Preparation often ranges from a few months to a year depending on prior skills and weekly study hours. Many candidates spend hundreds of lab hours practicing.
Is CEH practical or theoretical?
CEH covers practical techniques and tools but the exam format is knowledge based. Practical lab additions exist in some training bundles but the core exam is multiple choice.
Can CISSP be self studied?
Yes, many professionals self study for CISSP, but a robust study plan, official materials, and practice tests are recommended due to the breadth of content.
Should managers learn OSCP?
Managers benefit more from understanding OSCP outcomes rather than the full technical depth. Practical awareness helps managers set realistic expectations for pentest engagements.
How do I choose between CEH and OSCP?
Choose CEH if you want structured knowledge and a recognized base credential. Choose OSCP if you aim for a technical penetration testing role and want to prove hands on ability.
Are there prerequisites for CEH?
CEH has no strict prerequisites, though candidates with some networking and security basics will find preparation easier.
Does CISSP cover compliance topics?
Yes. CISSP includes governance, compliance, risk management, and legal topics across its security domains.
How often must I renew these certifications?
CEH, OSCP, and CISSP have renewal or continuing education requirements. CISSP requires continuing professional education credits and an annual maintenance fee. Check each body’s policy for current details.
Can I pursue all three certifications?
Yes. Many professionals progress through multiple certifications during their careers to combine tactical skill and strategic knowledge.
Where can I find recommended training for these certifications?
Look for accredited training providers, hands on labs, and community recommendations. Local and online Training options can help you pick suitable courses and practice environments.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0

















