How Do Hackers Exploit Browser Vulnerabilities?
Learn how hackers exploit browser vulnerabilities in 2025 using XSS, CSRF, clickjacking, SOP bypass, WebAssembly RCE, and extension abuse. Master real attack chains and defenses from the Ethical Hacking Institute.
Introduction
Over 4.7 billion users browse daily, making browsers the most attacked software in 2025. Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge process untrusted code from millions of websites, creating endless exploitation opportunities. Zero-day browser bugs sell for $1M+ on dark markets. From XSS stealing cookies to WebAssembly remote code execution, attackers chain vulnerabilities to bypass sandboxing and gain system access. This guide dissects real-world browser exploitation techniques, tools, and mitigation strategies. The Ethical Hacking Institute teaches browser security through isolated labs with vulnerable extensions, malicious sites, and custom exploits.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): The Gateway Drug
- Reflected XSS: Malicious payload in URL parameter
- Stored XSS: Script saved in database, served to all users
- DOM-Based XSS: Client-side JavaScript manipulation
- Session Hijacking:
document.cookietheft - Keylogging: Capture keystrokes on login forms
- Phishing Overlay: Fake login prompt over real site
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): Silent Actions
Exploits authenticated user sessions to perform unwanted actions.
Modern browsers mitigate with SameSite cookies, but legacy apps remain vulnerable.
| Attack | Payload | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Fund Transfer | Financial loss | |
| Password Change | POST to /changepwd | Account takeover |
Practice XSS/CSRF in Pune certification labs at the Ethical Hacking Institute.
Clickjacking: Tricking User Clicks
- UI Redressing: Transparent iframe over legitimate button
- Likejacking: Hidden Facebook Like button
- Camera/Microphone Access: Fake "Test Webcam" overlay
- File Upload Hijacking: Invisible file input
- Cursor Jailing: CSS traps mouse in attack zone
- Double Click Attack: Requires two precise clicks
Same-Origin Policy (SOP) Bypass Techniques
SOP isolates domains, but flaws allow cross-origin data access.
JSONP, CORS misconfig, and DNS rebinding enable unauthorized reads.
- CORS wildcard origins
- JSONP callback injection
- DNS rebinding attacks
- PostMessage misuse
- Universal XSS in browser
- Cache poisoning SOP bypass
Master SOP attacks via online courses at the Ethical Hacking Institute.
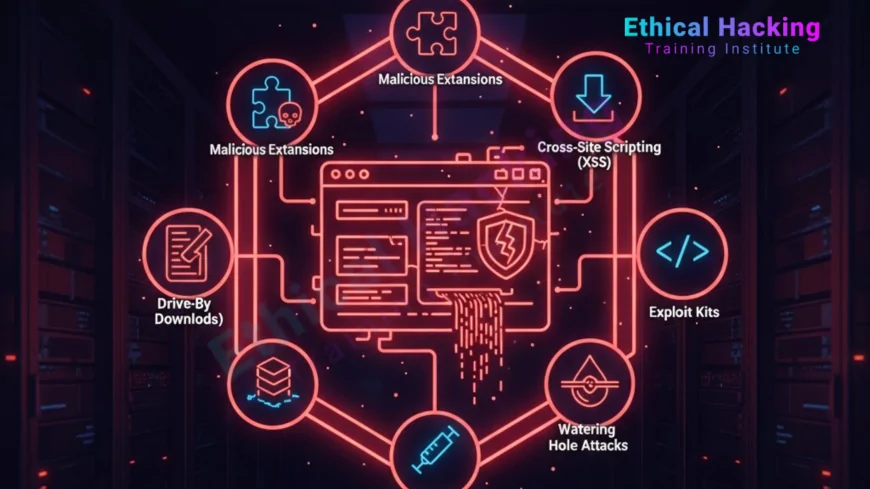
Malicious Browser Extensions
Extensions have high privileges: read all tabs, modify HTTP, access file system.
Supply chain attacks compromise popular extensions.
- Cookie stealing extensions
- Keylogging via content scripts
- HTTP request modification
- Phishing page redirection
- Crypto wallet draining
- Ad injection revenue
WebAssembly (Wasm) Remote Code Execution
- Memory corruption in Wasm runtime
- Buffer overflow exploitation
- Sandbox escape to browser process
- Native code execution
- Zero-click drive-by attacks
- Persistence via Service Workers
Browser Cache and History Attacks
Cache poisoning, deception, and history sniffing reveal sensitive data.
Attackers infer user behavior from timing and resource availability.
| Attack | Method | Data Leaked |
|---|---|---|
| Cache Poisoning | Malicious response | Fake content |
| History Sniffing | CSS visited links | Browsing history |
Explore cache exploits with advanced course at the Ethical Hacking Institute.
Fingerprinting and Tracking Beyond Cookies
- Canvas fingerprinting
- WebGL renderer details
- AudioContext oscillator
- Battery API status
- Font enumeration
- Hardware concurrency
Zero-Click Browser Exploits
No user interaction required. Visiting a site triggers full compromise.
Chains memory corruption with sandbox escape.
- Malformed WebP image RCE
- SVG filter use-after-free
- CSS parser heap overflow
- JavaScript engine type confusion
- V8 sandbox escape
- Renderer process takeover
Defending the Browser: Hardening Strategies
Layered defense reduces attack surface. No single control is sufficient.
Combine policy, configuration, and user awareness.
- Enable site isolation
- Use Content Security Policy (CSP)
- Deploy Subresource Integrity (SRI)
- Block third-party cookies
- Enforce HTTPS with HSTS
- Disable unnecessary plugins
Conclusion: Browsers Are Fortresses Under Siege
Browser vulnerabilities evolve faster than patches. In 2025, XSS, extension abuse, and zero-click exploits dominate real attacks. Defense requires secure coding, strict policies, and continuous monitoring. Users must disable unnecessary features and keep browsers updated. The Ethical Hacking Institute, Webasha Technologies, and Cybersecurity Training Institute offer hands-on browser security training with real exploit development. Start auditing your browser extensions today. The next click could be your last if security fails.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are browsers safe in 2025?
Safer than ever, but zero-days and misconfigurations persist.
Does incognito prevent tracking?
No. Only hides history from local user, not from sites.
Can XSS steal HTTPS cookies?
Yes, if not marked HttpOnly and Secure.
Is Firefox more secure than Chrome?
Different trade-offs. Both patch quickly; configuration matters.
Do ad blockers stop exploits?
Partially. Block malicious ads but not zero-click bugs.
Can WebAssembly be disabled?
Not easily. Required for modern web apps.
Are mobile browsers vulnerable?
Yes. Same engines, smaller attack surface but growing.
Does VPN protect browser?
Encrypts traffic but not browser logic flaws.
Can sandbox escape lead to system access?
Yes. Renderer compromise + sandbox escape = full control.
Are browser extensions safe?
Only from trusted sources. Review permissions carefully.
Does CSP stop all XSS?
Reduces risk but bypasses exist with misconfiguration.
Can history sniffing be prevented?
Modern browsers block CSS visited link styling.
Is clickjacking dead?
Reduced by frame-busting but still works on old sites.
How often are browser zero-days found?
Monthly. Google Project Zero reports dozens annually.
Where to learn browser exploitation?
Ethical Hacking Institute offers browser security and exploit dev labs.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0